The key notes from the book HTTP The Definitive Guide
1. HTTP: The Web’s Foundation
HTTP is a protocol that is popular with web applications. It helps to transfer billion of JPEG images, HTML pages, text files, audio,… everyday.
Each web resource has a name, and URI/URL is the unique address to point to that resource.
HTTP transaction consists of requests from the client and responses from the server. This communication happens with a formatted-block of data called HTTP messages.
HTTP messages will contain: Method, Request URL, Status Code, Header, Entity Body,…
HTTP is carried over TCP/IP connection.
- TCP connection: carries HTTP data in order (without corruption)
- IP -> point to the right computer
- PORT -> point to the right application
2. HTTP Architecture
A web server processes HTTP requests and save responses. The term “web server” can refer either to web server software or to the particular device or computer dedicated to serve the website. One common example is Apache.
Web robots are software programs that automate a series of web transactions with-out human interaction.
- Other names: crawler, spider.
- robots.txt: instruct robot how to crawl a website, what to include and exclude. Bot should retrieve robots.txt when they first visit the site.
- Robot also adhere to document meta tags such as: noindex, nofollow,…
- Canonical: a canonical URL will help robot to eliminate the aliasing problem of a website that different URLs alias to the same document.
The other elements of HTTP Architecture are: Proxy, Caching.
3. Identification, Authentication & Security.
There are some approaches to help to identify a user on the website by using: HTTP Header, check client’s IP address, user login, fat URL, Cookies (best).
Authentication:
- Basic authentication: use username + password on the authorization header. Maybe encoded as base64.
- Digest authentication: instead of sending username and password. This will sent a fingerprint that generated by functions such as MD5.
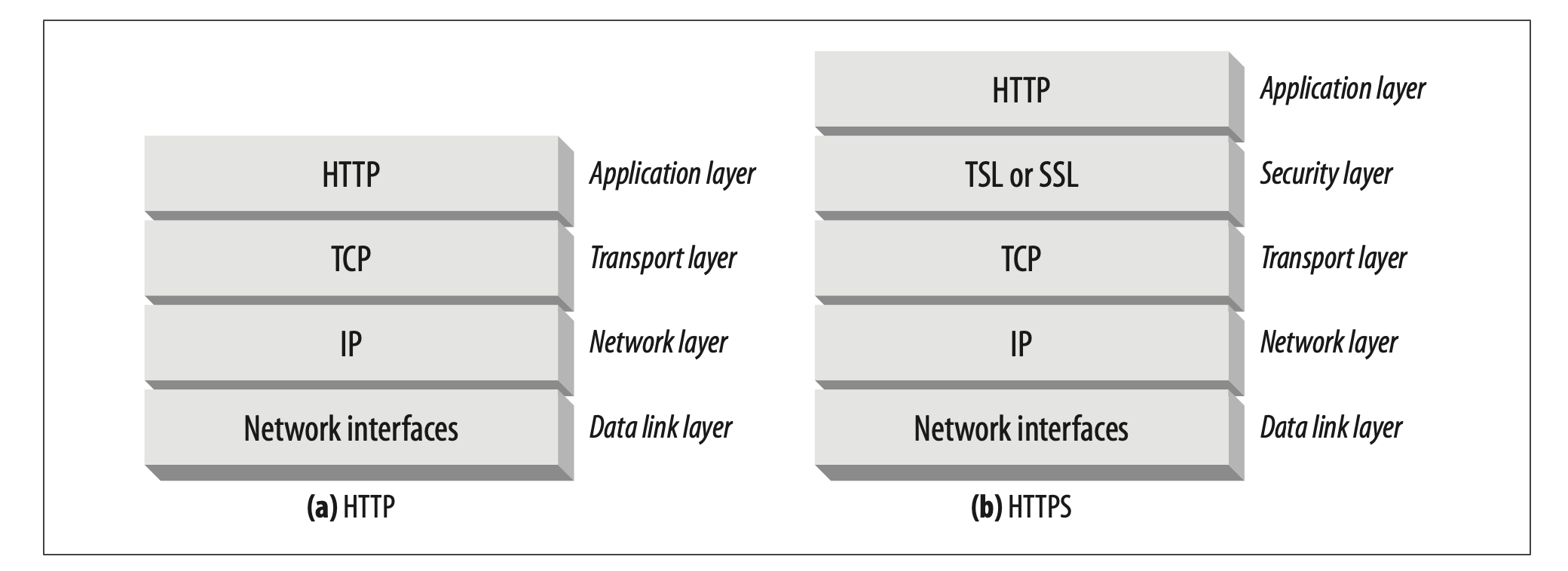
Secure HTTP:
- HTTPS: all HTTP requests/responses is encrypted before being sent. HTTPS works by providing a secured layer (SSL).
- SSL certificates are used to authenticate servers and establish a secure connection between the client and the server. The certificate includes: hostname, public key, signing authority, signature…
4. Entities, Encodings, and Internationalization
This chapter describes the formats and syntax of HTTP content.
“Messages Are Crates, Entities Are Cargo”
The URL should only contain US-ASCII character set. With those characters that are not safe. We have an encoding mechanism by using an “escape” notation (% + 2 hexadecimal that represent the ASCII code of the characters).
5. Content Publishing and Distribution
Part V talks all about the technology for publishing and disseminating web content.
The hosting service use a one big physical server and to share with others if one client doesn’t really need a whole physical server.
The problem with one server is that it might break due to some specific reasons. And here’s the mirrored server farms come to cover each others.
CDN (content distribution network) is simply a network whose purpose is the distribution of specific content. the nodes of network can be web servers, surrogates, proxy caches. Example: Cloudfare, AWS Cloudfront,…